Análisis de la acción/intención motora mediante el estudio de las señales EEG
Imágenes
 Fecha: septiembre 2019
Fecha: septiembre 2019
Autor: Nabil Ajali Hernández
Tutores: Carlos M. Travieso González
Resumen del TFM:
En la actualidad, gracias a los avances en computación se han desarrollado campos como la domótica, las Smart cities, la inteligencia artificial, el diagnostico en medicina y otras muchas en lo que se conoce como Internet of Things.
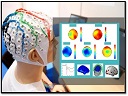
En el presente trabajo, de manera paralela a universidades vanguardistas, como la universidad de Stanford (que ha presentado nuevos estudios sobre el análisis de intención motora utilizando inteligencia artificial), se adquiere una base de datos de la página Physionet.org que contiene archivos con la señal del electroencefalograma de 109 usuarios. Estas señales, son registradas mientras los sujetos realizan pruebas motoras y pruebas de intención motora (pensar en realizar una acción). Posteriormente, se procesa la señal de las pruebas y se le aplican una serie de transformaciones y cálculos que permiten la clasificación de la acción e intención motora al utilizar los algoritmos de aprendizaje (Machine Learning) para el diseño e implementación de una red neuronal, ver figura 1.
Los resultados reflejan que la red neuronal es capaz de detectar con porcentajes superiores al 78% si el sujeto está realizando o tiene intención de realizar un movimiento con la mano derecha o con la izquierda, siendo ligeramente superior el éxito del movimiento real (2.3% superior). Algunas de las posibles líneas futuras para mejorar la red incluyen ampliar los parámetros estadísticos utilizados, aplicar PCA, variar los parámetros de los filtros e implementar otro tipo de sistemas de Deep y Machine Learning.
Nowadays, thanks to advances in computing, fields such as domotic (home automation), smart cities, artificial intelligence, diagnostics in medicine and many others have been developed in what is known as Internet of Things.
In this work, parallel with the forefront universities, such as Stanford University (which has presented new studies on the analysis of the motor intention using artificial intelligence), a database of the page "Physionet.org" is acquired. This database contains files with the electroencephalogram signal of 109 users. The signals are recorded while the subjects perform motor tests and motor intention tests (think about performing an action). The signal of the tests is processed subsequently and a series of transformations and calculations are applied. This allow the classification of the action and motor intention using learning algorithms (Machine Learning) for the design and implementation of a neural network, see Figure 1.
The findings of this work reflect that the neural network developed is able to detect with percentages higher than 78% if the subject is making or attempts to perform a movement with the right hand or with the left, being slightly higher the success of the real movement (2.3% higher). Possible future lines to improve the network include expansion of statistical parameters used, applying PCA, variation of filters parameters and implementing other types of Deep and Machine Learning systems..